ASME Compliance: Understanding Pressure Vessel Fabrication
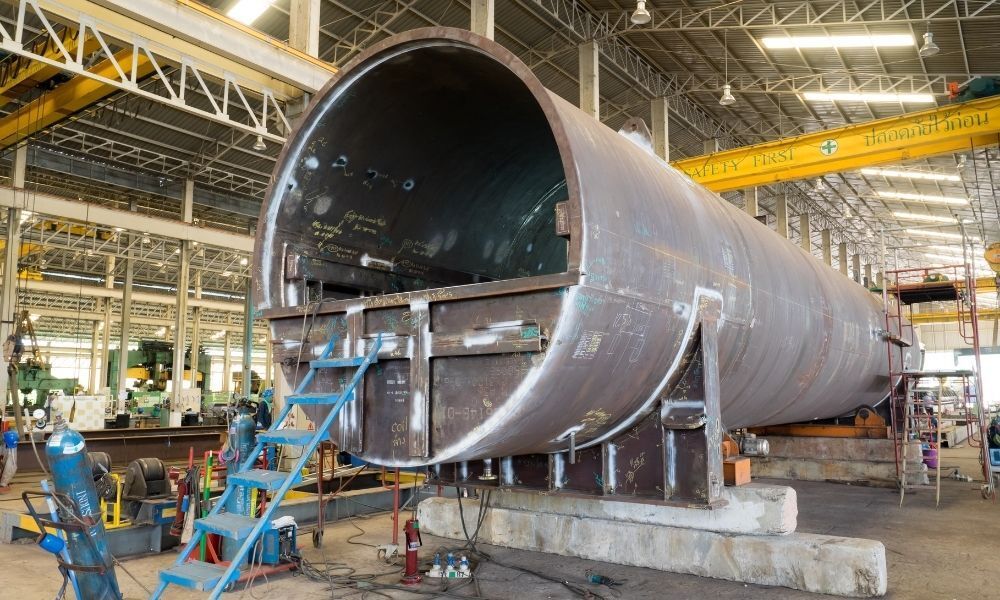
To sum everything into one, pressure vessel fabrication is a complex process that requires precise cutting. The process is controlled by cutting, bending, welding, and piecing together metals for vessel fabrication. It’s an essential process that is commonly found within ASME compliance for understanding pressure vessel fabrication. Here is our list of everything you need to know to understand pressure vessel fabrication better and comply with ASME standards.
What Is ASME?
ASME stands for the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The society began in 1880 to house working-class knowledge and courses on building the right skills for standard metal fabrication processes. The association continues to promote the necessity for engineers in our civilization.
Considered a code, ASME is the official stamp to show approval for the design, development, and construction of boilers and pressure vessels maintained in many industries. The ASME code has three parts, each describing the basic requirements for ASME compliance for pressure vessel fabrication. All pressure vessel manufacturers need to refer to these sections during their work stages.
Part I
This part comprises three subsections; it helps lay out specific banned and required necessities that are key to providing accurate designs for the manufactured pressure vessels.
Subpart I
Subpart I describes the standard requirements concerning materials and construction. This includes any material needed for designs or openings and others facets, such as markings, reports, and overpressure protection.
Subpart II
Subpart II describes requirements that relate to pressure vessel manufacturing. Some parts reference fabrication techniques used for ASME vessels, such as welding, forging, and brazing. This subpart will help you better understand the materials and fabrication processes used and how inspection and other areas play a role in following and understanding the pressure vessel fabrication process.
Subpart III
The material classes are explained in this subpart. You can use pressure vessels with low alloy and carbon steels, high alloy steels, and more. All mandatory requirements for building a pressure vessel from usual materials will be listed here.
Part II
Once you open part II, you'll notice that it lays out all requirements for your pressure vessel's design, fabrication, engineering, and testing. The vessel needs to be able to endure both internal and external pressures. This section will also go over using UV and U2 designators.
Part III
The final part will cover all there is to know about what to exclude in the design, fabrication, engineering, and testing of a high-pressure vessel. All pressure vessels will need to be able to resist internal and external pressures. This section also covers what to know when using U3 and UV3 designators.
Understanding each part’s role in these processes and being able to apply them to your engineering work is crucial. This knowledge is mandatory when working alongside manufacturing companies like Custom Manufacturing and Polishing Inc., which works closely with ASME pressure vessel fabrication. Custom Manufacturing and Polishing Inc. will provide the right services that meet all ASME pressure vessel fabrication codes and requirements.